Content:
The normal growth and development of lilies can be impaired due to the development of diseases. Before starting the fight against them, you need to know what lilies are sick with and how to treat them.
Some symptoms of diseases
- Web.
This symptom is typical for spider mites. These pests consume plant sap, which inhibits plant growth. The foliage begins to curl and soon dries up. The presence of a tick can also be identified by a white coating and a pile of laid eggs.
- Rust.
This symptom is typical for a number of fungal diseases, but most often it occurs in the presence of rust - the disease of the same name. First, small colorless dots are formed, which soon turn red. This provokes drying of foliage and stems.
- Why do lilies disappear after winter or shrink.
Most often, this is not caused by diseases, but by poor-quality planting material in conjunction with a late planting. Often during this period, bulbs are sold that were stored in refrigerated chambers throughout the spring and summer. After planting in open ground, they begin intensive growth, which does not have time to complete by winter. Such plants are damaged by frost and most often die, and if they survive, they will become smaller and weaker, that is, they degenerate. This is the main answer to the question of why lilies degenerate, and also why lilies do not bloom and shrink.
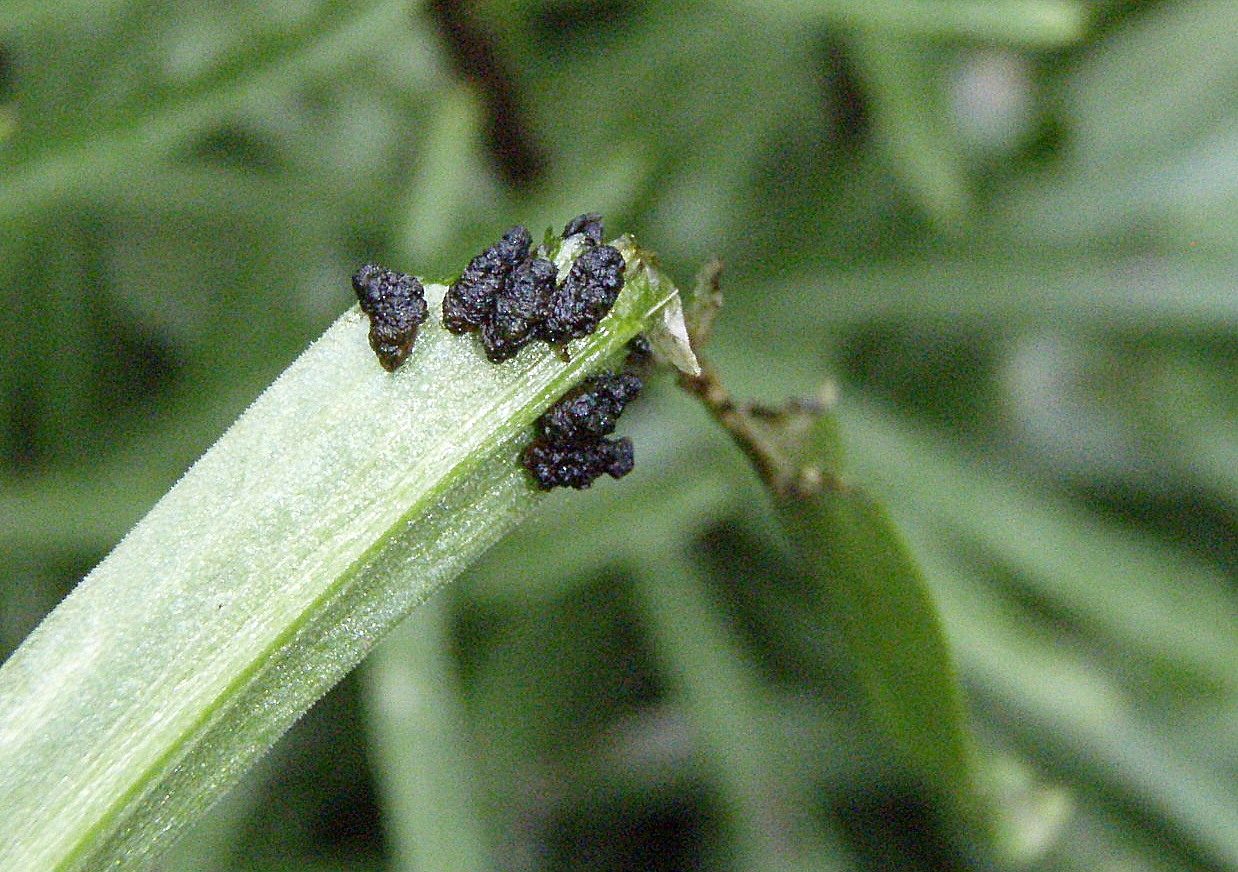
Black balls on lilies - what is it? The presence of small black balls at the base of the foliage is often mistakenly recognized as a symptom of another disease. However, this sign is not a symptom of the presence of a disease and pest on the lily. In fact, black lumps on lilies are bulbs (babies). As they ripen, these peas will fall off and begin to grow, as a result of which new plants will be formed.
Lily diseases and their treatment
Gray rot (botrytis)
When answering the question of what lilies are sick with, it should be noted that this is the most common fungal disease, the pathogens of which are located on plant residues in the soil and, under certain conditions, are capable of starting harmful activity. At first, the disease attacks the lower leaves, which turn yellow and subsequently fall off.
In the presence of warm weather and strong moisture, botrytis on lilies instantly spreads over the plantings, damaging all plant organs. Moreover, even with significant damage, the plants rarely die, but they completely lose their decorative properties. The bulbs remain the same externally, but they stop growing in size. A year later, they will sprout again.
Plants growing in low, insufficiently ventilated areas are most often affected by the disease. In the presence of high humidity, the diseased parts of the lily are densely covered with a grayish coating, which is a fungal sporulation.
Botrytis on lilies: how to treat? The disease can be cured using systemic fungicides, which are applied immediately after the first symptoms of the disease are detected. The disease can be most quickly treated with Topsin-M and Fundazol.Treatments with these agents alternate with spraying with copper-based preparations: oxychom, Bordeaux mixture, etc.
Fusarium lily
One of the most common diseases on garden and indoor lilies. According to the description, it begins its distribution from the underground organs of the peduncle. They are covered with a large number of oblong markings in various shades of red and orange. As the disease progresses, it spreads up the stem. The foliage at the same time acquires a slightly purple color, and as it dehydrates, it quickly turns yellow.
In severe cases, the bulb can also get sick. The underground roots of this organ acquire an unhealthy brownish-brown color. Putrid foci begin to form on the scales, which are covered on top by mycelium in the form of a pink bloom. During the digging, the affected bulbs fall apart, and their fragments remain in the ground, on which the pests of the disease are abundantly located. After that, it is not recommended to cultivate not only lilies on this site for five years, but in general all bulbous crops.
If the bulb becomes sick with Fusarium, then this often does not affect the condition of the root of the plant. It can look healthy and grow normally thanks to the roots above the bulb. Despite this, with the onset of autumn, culture dies. Such a plant can subsequently be revived from children that are located in the area of the flowering base above the roots.
In order to get rid of the disease, seed material is etched in potassium permanganate or in a solution of a systemic fungicide before planting. In autumn and spring, the affected plot is disinfected with 300 grams of ferrous sulfate, dissolved in a 10-liter container with water. After planting, dolomite flour is added to the plot.
Cercosporosis
With this disease of lilies, the ends of the leaves are covered with small marks, which over time increase in size and occupy an ever larger area of the plant. They are usually yellowish-brown in color with dark edging.
To the question of how to process lilies, it should be answered that in the presence of these symptoms, 1% Bordeaux liquid is used, as well as the fungicides Hom, Abiga-Peak or Topaz. In the spring, at the beginning of the growing season, prophylactic agents such as Fitosporin-M are used. Every three weeks, the plantings are treated with Gamair or Alirin, 2 tablets of which are diluted in 10 liters of water and mixed thoroughly.
Anthracnose
Brownish-dark marks form on the foliage, which in advanced cases spread throughout the lily up to the bulb. A black shapeless border is formed around these spots.
Most often, fungicides such as Rovral (1 gram of the drug per 1 liter of water), Fundazol (15 g / 10 L of water) are used to treat the disease. The use of Topsin-M has a good effect. All affected leaves should first be torn off to stop the further spread of the disease.
Fitium
With this disease, the upper part of the leaves turns yellow, as a result of which the entire plant gradually dries out. The rhizomes are first densely covered with brownish marks, and subsequently rot.
Treatment begins with cutting off all affected plant organs. Before planting, a 0.2% Fundazole solution is prepared and the planting material is placed there for 30 minutes. The soil is pre-disinfected with a 0.4% solution of colloidal sulfur.
Disease prevention
The main method of prevention is the use of only those varieties of lilies that are resistant to the main diseases of the crop. It is desirable that at the same time they were zoned in the intended region of cultivation.The planting material must be strong and healthy. You can improve his condition by soaking in a particular preparation for an appropriate period of time.
The lily should be grown in accordance with agricultural techniques. First of all, it is important to observe spatial isolation both between rows and between plants in a row. It is necessary to choose the best site for the crop, which would not be located in low-lying areas with high humidity.
Watering should be sufficient but moderate. Top dressing should be applied in a timely manner, strictly observing the dosage. This is especially true of nitrogenous elements, which in excess amount provoke an increased growth of the vegetative mass. This makes the lily more susceptible to disease.
Pest control
Purple bulbs are characterized by a rich nutritional composition, as a result of which they are often attacked by various harmful insects. These pests damage plantings by destroying bulbs and foliage. At the same time, they spread dangerous viral diseases.
The most dangerous and common among them are:
- onion leaf beetle;
- red beetle;
- aphid;
- nematode.
Onion leaf beetle
This pest is an orange-colored and oval insect. There are about 20 points on its elytra. Both pupae of this insect and adults spend the winter in the ground and crawl out to its surface in the last days of April. The pest usually either eats the foliage from the edges or gnaws holes inside them.
A preventive measure against the pest is the timely destruction of weeds on the site, since it is on them that adults lay their larvae. Insects are harvested manually or destroyed using appropriate insecticides (Chlorophos, etc.).
As a folk remedy, an infusion based on larkspur or wormwood is used. To prepare the first option, a kilogram of finely chopped grass is dissolved in a bucket of water and left to infuse for 2 days. After spilling through the filter, the substance is ready for use as directed. A wormwood preparation is prepared by dissolving 800 grams of dried wormwood plant material in chilled water or a full bucket of fresh chopped grass. The solution is insisted throughout the day, after which the container with the solution is placed on fire for 30 minutes. Immediately before spraying, the resulting product is mixed with clean water in equal proportions. Several treatments are carried out, between which a week must pass.
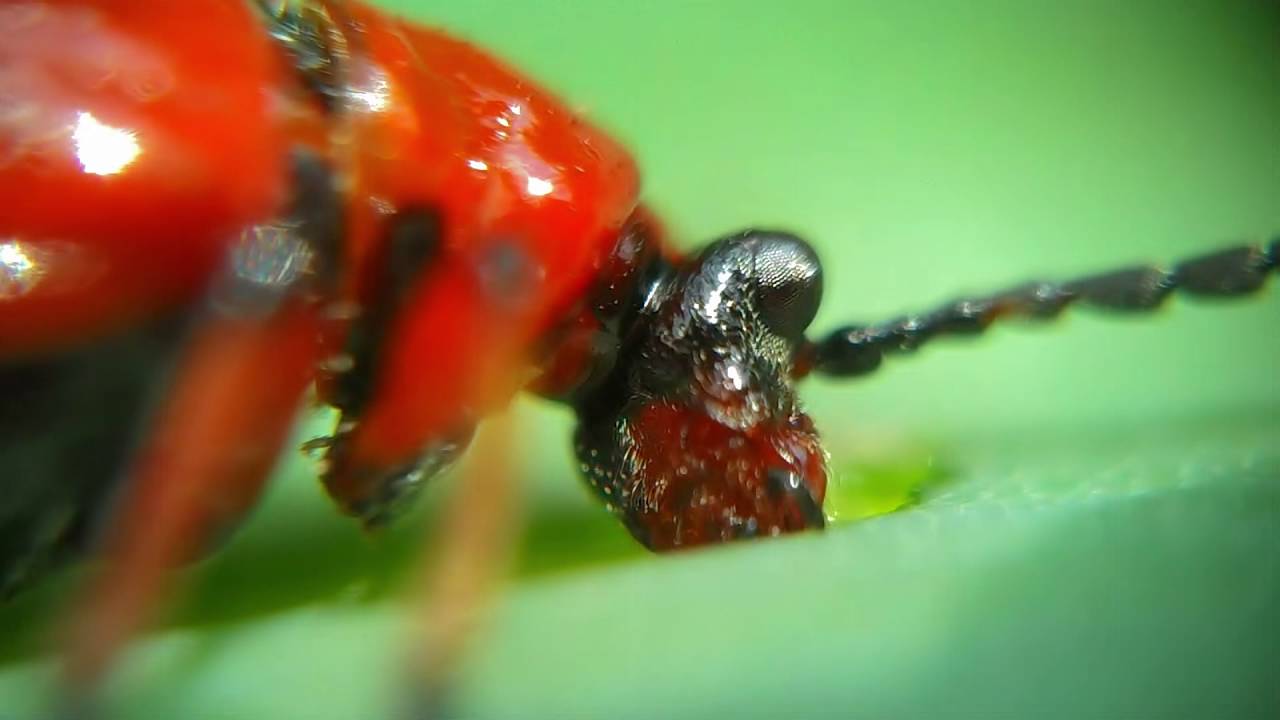
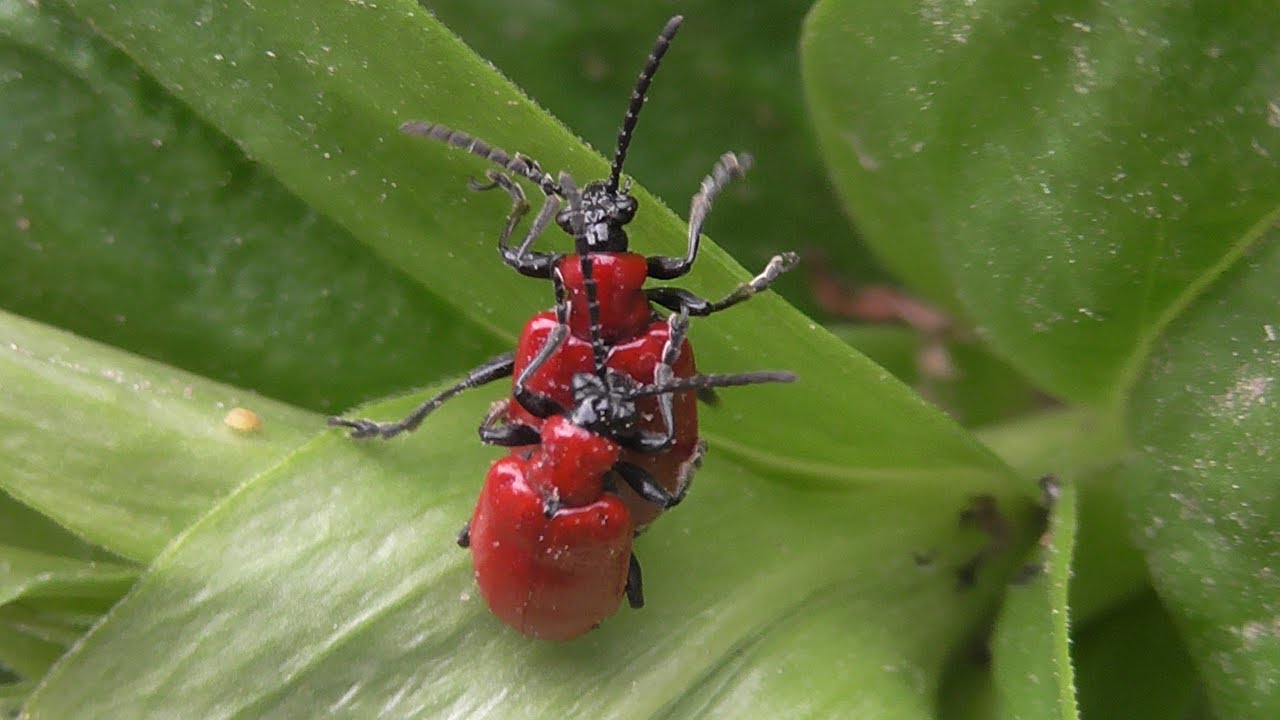
Red beetle
It is considered an unusually gluttonous pest that can destroy foliage, bulbs and lily inflorescences. Adults are found on plantations from April and, in the absence of proper control, soon spread the larvae throughout the site. Insects are usually harvested by hand and subsequently destroyed. If the pest population is too high, then any insecticide is used against the Colorado potato beetles, for example:
- Confidor;
- Aktara;
- Decis.
Aphid
The insect not only directly harms plants, but also serves as a carrier of viral infections. In view of this, the pest must be promptly and quickly destroyed. For this purpose, it is recommended to use drugs such as Intavir or Fufanon.
Nematoda on lilies
Small round worms that live in the ground. Insects develop inside plant tissues. As a result, tumors and growths form on the stems and foliage. Cracks of varying depth are formed on the trunk, and the inflorescences are severely deformed. Only by these external symptoms can the presence of the pest in question be determined.
Treatment consists mainly of disinfecting the soil in the plot.Damaged plants are dug up and destroyed on the spot using fire.
Having studied the main diseases and knowing how to treat lilies, you can effectively fight against ailments and keep the plantings in a healthy state. Such plants will delight gardeners and summer residents with lush, long flowering.