Content:
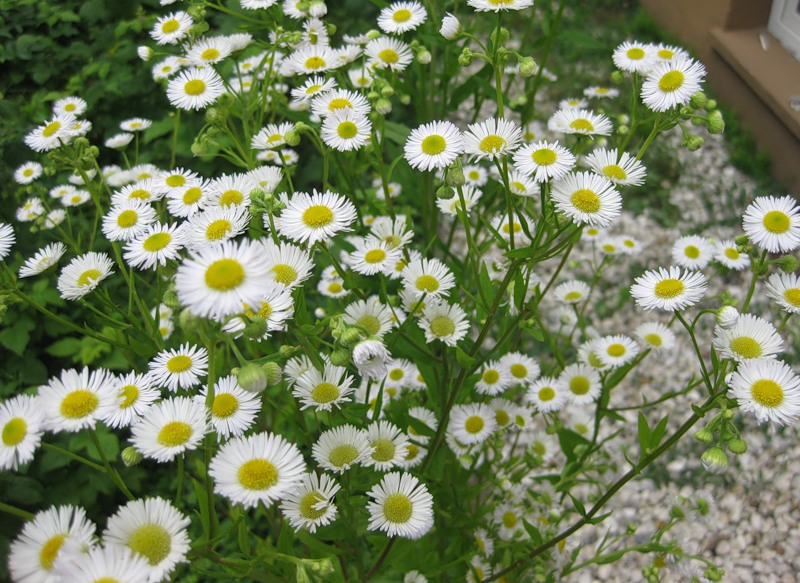
Small garden chamomile, or Pyrethrum, is a perennial flowering plant of the Asteraceae family, widely used for various purposes. Due to the external similarity, chamomile is often confused with other plants of the Astrov family: gerbera, chrysanthemum, daisy.
The first mentions of chamomile date back to the eighteenth century, even then scientists noticed the medicinal properties of this plant and began to use it in the treatment of gynecological diseases. To this day, undersized chamomile is used in medicine: inside in the form of tea or tincture, for diseases of the stomach, intestines, and also as an anti-inflammatory and diaphoretic.
In addition to medicinal purposes, chamomile is widely used in gardening. It is planted both separately and in combination with other wildflowers, grown to create bouquets, ikebans and floristic compositions.
Plant characteristic
Representatives of the genus are low (on average about 50-70 cm in length) plants with pinnately dissected leaves, inflorescences are baskets with a yellow center and white petals located along the edges.
Low-growing small chamomile is mainly perennial, but there are also annual species. The root is tap-type, weakly branched, but deeply deep. The fruit is a small oblong achene.
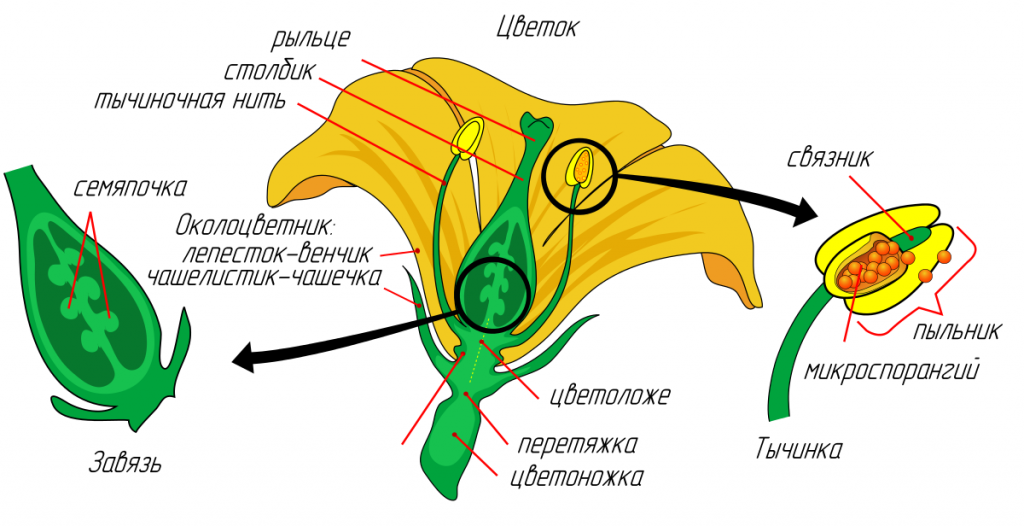
The process of pollination in daisies is very interesting: the anthers open from the inside, the pollen enters the tube, which is formed from the accreted pollen sacs. The pistil, which is not prepared for fertilization, is still pushing the pollen out. The pollen lump sticks to insects that have flown in to feast on sweet flower nectar, and only when the pollen completely runs out of pollen does the pistil ripen, which is pollinated by pollen from neighboring, younger flowers.
Chamomile does not belong to primroses, since it blooms much later than the snow melts. The flowering period lasts from late spring to early or even mid-autumn. It is because of the long growing season that chamomile is so loved by many domestic flower growers.
Characteristics of species and varieties of crops
In addition to the fact that small chamomile (another name is Pyrethrum) has many names, they include more than a hundred species. Most often, about fifty are used in floriculture, descriptions of some of them:
- Hybrid feverfew is the progenitor of all subsequent species. It can be both large enough and small flowers of various shapes and colors of petals: red, yellow, pink, and so on.
- Maiden feverfew (maiden tansy) is a strongly branched plant approximately 50 cm high. It differs from other species in smaller petals. In floriculture, tansy varieties with double spherical flowers no more than 5 cm in diameter, resembling chrysanthemums, are highly valued.
- Pyrethrum scutellum (meadow chamomile) - single stems, baskets are collected in thyroid inflorescences. It has no hybrid varieties, the color of the petals is most often white.
- Dalmatian chamomile - it has a bright pink color of petals and a small size of shoots, only about 50-60 centimeters.It is recommended to plant at the edges or in the center of the flower bed, then during flowering, bright, eye-catching petals will be especially noticeable.
There are several ways to plant small daisies. The most common is using seeds.
Features of planting and crop care
In April-March, seeds are planted to a depth of 3-4 mm, kept at a temperature of at least 20 degrees, after which they dive into pots or special peat cups, in which the shoots are then planted in the ground. Young shoots are able to withstand small frosts, and adults can easily tolerate a slight minus temperature. In the southern regions, it is possible to plant seeds directly in the beds, this is done in late August and early September.
Feverfew prefers loose soil, rich in nutrients. Do not plant it in dry, sandy or clayey infertile soil. Low-lying places with stagnant water are also not suitable; garden chamomile does not like abundant moisture, especially at low temperatures. Ideal would be a place in the shade that is under the sun for only a few hours a day.
Pyrethrum should be planted at a distance of 20-30 cm from each other, the first weeks they need abundant watering. Perennial plants begin to bloom the next year after planting.
Caring for small chamomile is easy, so this plant is ideal for those who do not have a lot of time to work in the garden. The only thing a plant needs is systematic watering. Pyrethrum copes well with weeds on its own, they need to be removed only during the growing season, then loosen the ground a little in order to avoid the formation of a dense crust that prevents water from reaching the root.
Feverfew is fed with various mineral fertilizers, but you should not use nitrogen fertilizers: in this case, the plant will only grow the green part, and the flowers will become small and rare. Organic fertilizers such as manure or humus are also great for chamomile.
After the first flowering, it is recommended to remove all inflorescences without waiting for the seeds to prevent re-flowering.
Major diseases and pests of crops and control measures
Bush garden chamomile is extremely rare. Most often these are fungal diseases, when a gray bloom appears on the leaves of individual plants. In this case, the affected bush should be removed as soon as possible, and the soil and remaining plants should be treated with a fungicide with copper.
An insecticide treatment usually helps to get rid of all types of parasites. There is also a more natural way - to attract animals such as hedgehogs and birds to your site, which love to eat slugs or insects.
Small garden daisies, as feverfew is often called among the people, will not cause much trouble in care, but for a long time they are able to decorate gardeners' plots with bright beautiful flowers.