Content:
The emergence of new varieties of apricots that can be grown in the conditions of the northern regions of Russia became possible thanks to the tireless work of Russian breeders. Although such species appeared relatively recently - at the beginning of the 21st century - they are already grown in many gardens in the Urals, Siberia, the middle belt and the Moscow region.
One of these wonderful varieties is the Aquarius apricot. Its positive qualities, early maturity and other characteristics will be discussed below.
General information about culture
This apricot variety was obtained in the main botanical garden of our country, where a description of this stone fruit tree was presented. The breeder who was engaged in the breeding of a new varietal culture - Kramarenko L. A. Apricot Aquarius was created thanks to the free pollination of apricot "Lel". Work on its breeding began in the 90s of the last century, and the Apricot Aquarius was entered into the State Register in 1996.
This apricot is highly resistant to severe frosts, therefore it is zoned for cultivation in the Central, Central Black Earth regions, the middle lane and other regions with a similar climate.
Apricot Aquarius: variety description
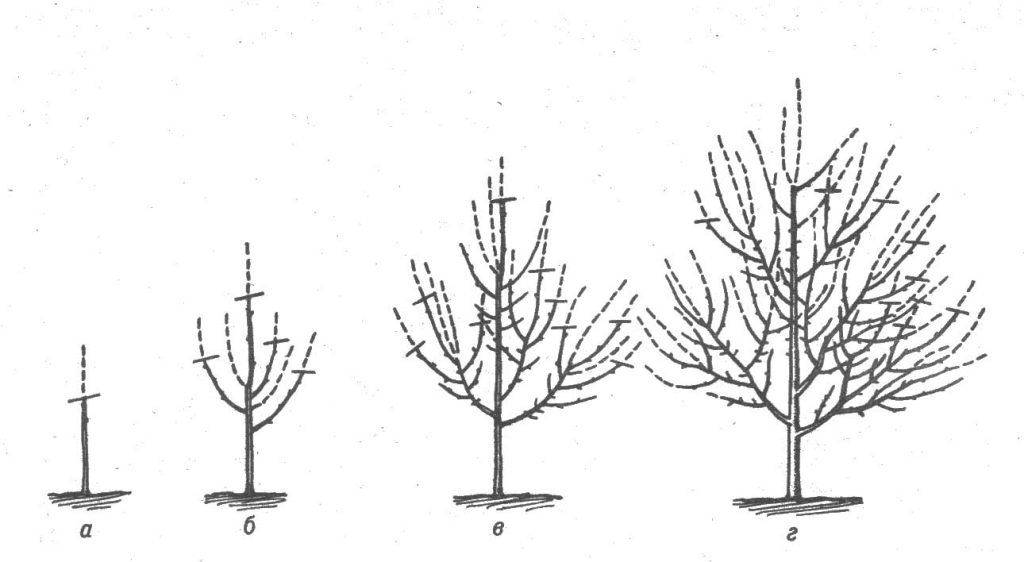
This plant is very tall - up to 5.5-6 meters.
- The color of the bark of the trunk is red with a brown tint.
- The branches are straight, grow well, creating an average crown in volume.
- The foliage is large, dark emerald, rounded, the ends are sharp. The veins are almost invisible.
This variety is highly resistant to frost and can easily withstand frosts down to -35 ° C without freezing. And from the "parent" tree Aquarius took high resistance to drought.
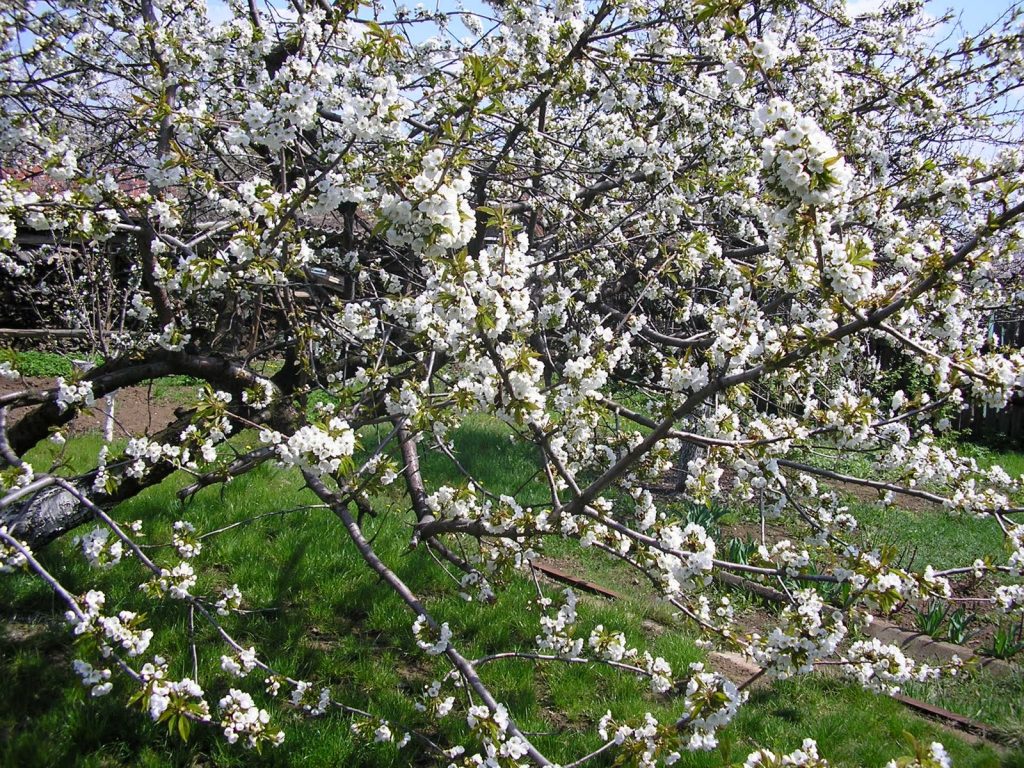
The tree looks especially beautiful in spring at the time of flowering, when the bare shoots are completely covered with small white flowers with a pink tint. Each bud has five petals. During flowering, the flowers exude a pleasant aroma that actively attracts bees.
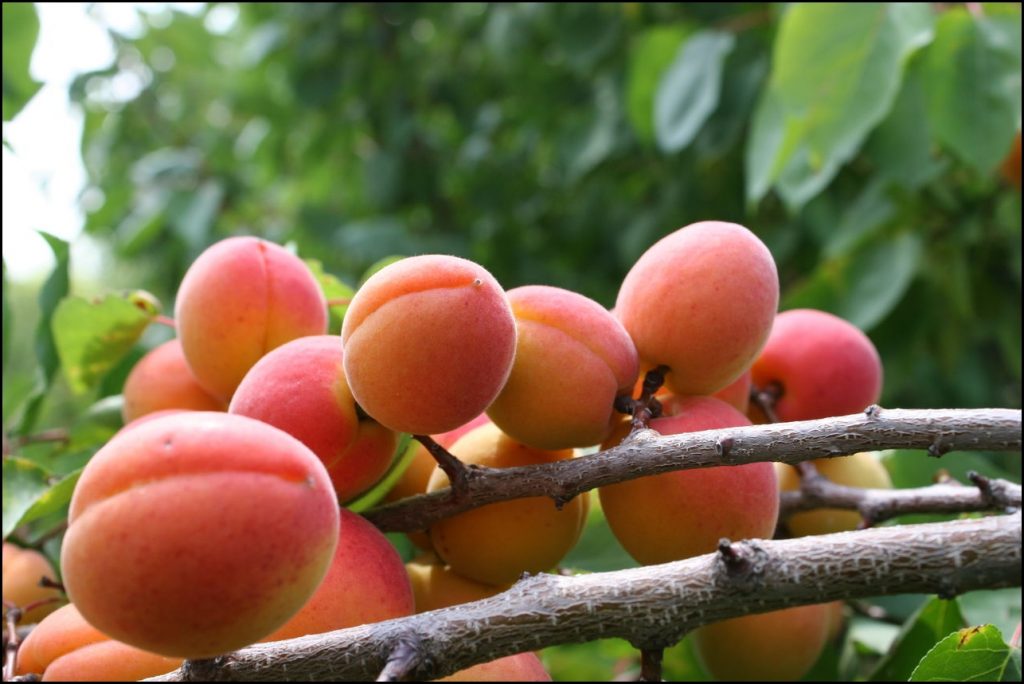
Ripe apricots can weigh about 25 g - this is a large size (compared to many other varieties). Fruit color - from pale yellow to deep orange. A small fluff is clearly visible on the skin. The skin is thin, practically not felt when eaten. The pulp is of medium density, orange in color, the stone is less than medium in size, in ripe apricots it separates well from the pulp.
Apricots Aquarius taste sweet, juicy, but slightly sour. Ripe apricot contains about 7.5% sugars and up to 2.8% acids. The first harvest from this apricot can be harvested three seasons after planting the seedlings in a permanent place. Young trees give no more than 12-14 kg of fruit, but in the future their yield increases to 25-28 kg. Amicable ripening of fruits begins in the second decade of August.
With good and timely care, all preventive measures are taken, this apricot bears fruit for 17-19 years, but sometimes longer.
The disadvantages include poor storage of the harvested crop. Fruits do not tolerate long-term transportation. At the same time, the commercial qualities of the fruit become worse, and the taste changes.
The harvested crop is used fresh, dried and frozen. Compotes, preserves and jams are especially aromatic.
To the main diseases in Aquarius, resistance is slightly higher than average (including perforated spotting).
Agricultural technology of cultivation
Planting seedlings in open ground can be carried out in the spring after the snow melts and the earth warms up (but the buds on the trees have not yet begun to bloom). But in the autumn period, this apricot can also be planted in September or early October.
In order for young trees to take root faster, it is necessary to prepare a place for planting them in advance. The site should not be shaded, but at the same time protected from wind gusts. The requirements for the soil are looseness, no stagnant moisture, with good drainage.
The acidity of the soil should be neutral (maybe slightly alkaline). The groundwater level should not come close to the surface of the earth.
The nature of this apricot variety is special, it is considered an "individualist", therefore it cannot stand most fruit trees next to it - the distance to them should be at least 8-9 m.
The exceptions are:
- cherry plum;
- turn;
- dogwood;
- other varieties of apricots are pollinators;
- some vegetable crops.
Before planting, in a couple of weeks, planting pits are prepared, the diameter of which should be about 0.7 m, and the depth - up to 0.8 m.
A drainage layer up to 5-7 cm thick is laid out on the bottom. The next layer is a mixture of soil, high peat and river sand. A seedling is placed in the center of the prepared hole, the root system is straightened and covered with soil. Then, about 20-25 liters of water are poured under each seedling.
In the spring, the apricot is pruned, removing frozen, damaged, broken off and dry shoots. Too long branches also shorten a little. Places of cuts must be covered with garden pitch.
Young trees planted in spring should be watered throughout the summer season - the top layer of the trunk circle should not be dry. But from the last ten days of August, watering must be stopped to allow the plant to prepare for the onset of cold weather.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The main positive qualities of this variety include:
- high resistance to frost;
- self-fertility;
- yields are high, regular;
- the taste of the fruit is excellent;
- the tree is resistant to damage by perforated spotting, and is also not affected by aphids.
This apricot has few drawbacks: the tree grows too large, and the harvested crop does not tolerate transportation well.
Undoubtedly, the Apricot Aquarius deserves the close attention of gardeners living in regions with frosty winters - after all, it does not need to be covered in autumn, and in spring there will be no traces of freezing. High yield and self-fertility are the reasons why summer residents should grow it on their plots.