Content:
The fruits of the apricot tree are used fresh and for processing. There are many opinions about the origin of the culture. According to one version, the plant was brought from Ancient China. Another hypothesis claims that it spread throughout the world from Armenia. This is confirmed by the second name of the culture - "Armenian apple". Discussions on this matter are still ongoing, because there is no conclusive evidence in favor of any version.
Fruit value
The fruits are used for food both fresh and dried. In addition, various homemade preparations are prepared from the fruit:
- compote;
- jam;
- jam.
Apricot pulp contains a wide range of vitamins and minerals:
- vitamins B1, B2, B15, C, P;
- provitamin A;
- tannins;
- pectin;
- inulin;
- iron;
- iodine;
- manganese;
- citric and malic acid;
- sugar up to 20%.
The fruit is characterized by a low calorie content. Apricot pulp supplies the body with a rich complex of substances and has a positive effect on health.
- pectin - lowers cholesterol and fights obesity;
- iodine - protects the thyroid gland;
- iron - increases hemoglobin;
- tannins have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Fruits promote blood formation, smooth heart function, stimulate the intestines. Why is it good to take fresh juice? It inhibits putrefactive bacteria and serves as a natural antibiotic. But, despite all the positive qualities, there are contraindications. You can not eat fruit on an empty stomach. In addition, eating large amounts of fresh fruit can be laxative.
Dried fruits
In a dried product, the percentage of various types of sugar increases to 80%, which makes it very different from fresh.
In these cases, you can use dried apricot infusions. They will help to cope with such problems:
- kidney inflammation;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Decoctions have good diuretic properties, they are able to relieve excessive puffiness.
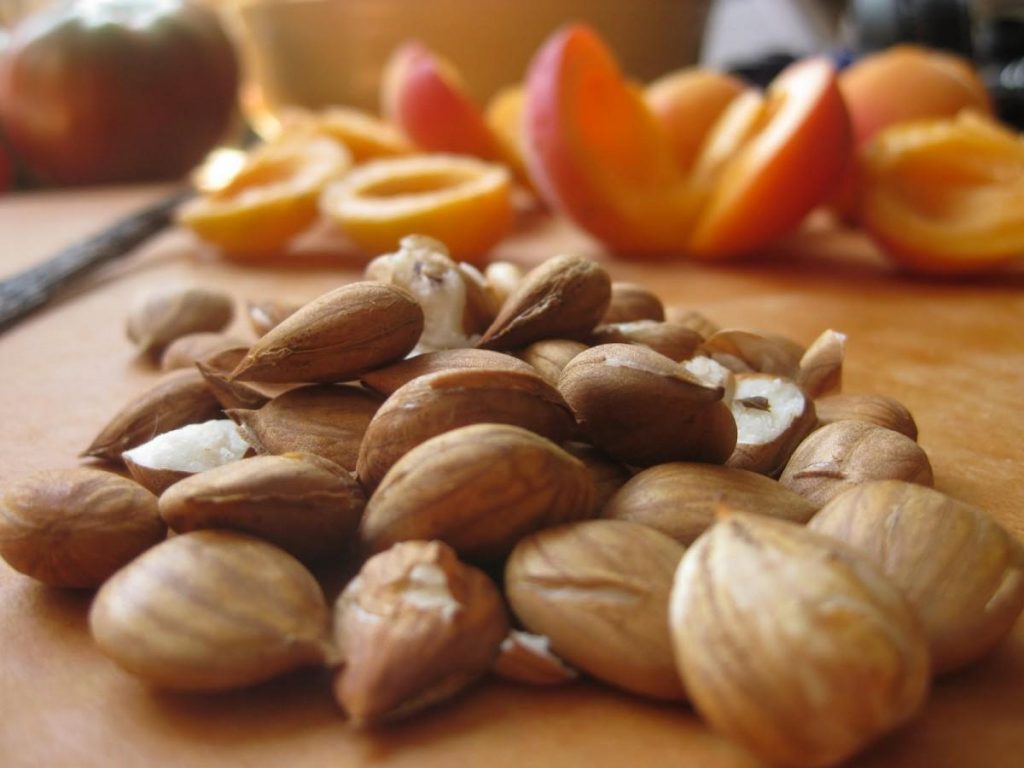
Apricot pits
Apricot pits are almonds. In oriental medicine, the nucleolus is used in inflammatory processes of the upper respiratory tract.
BJU apricot:
- proteins over 10%;
- carbohydrates up to 75%;
- fixed oils.
Basically, apricot seeds are processed to obtain oil, it is used to dissolve medicines. It contains acids in the following ratio:
- linolenic - 20%;
- stearic - 15%;
- myristic - 5%.
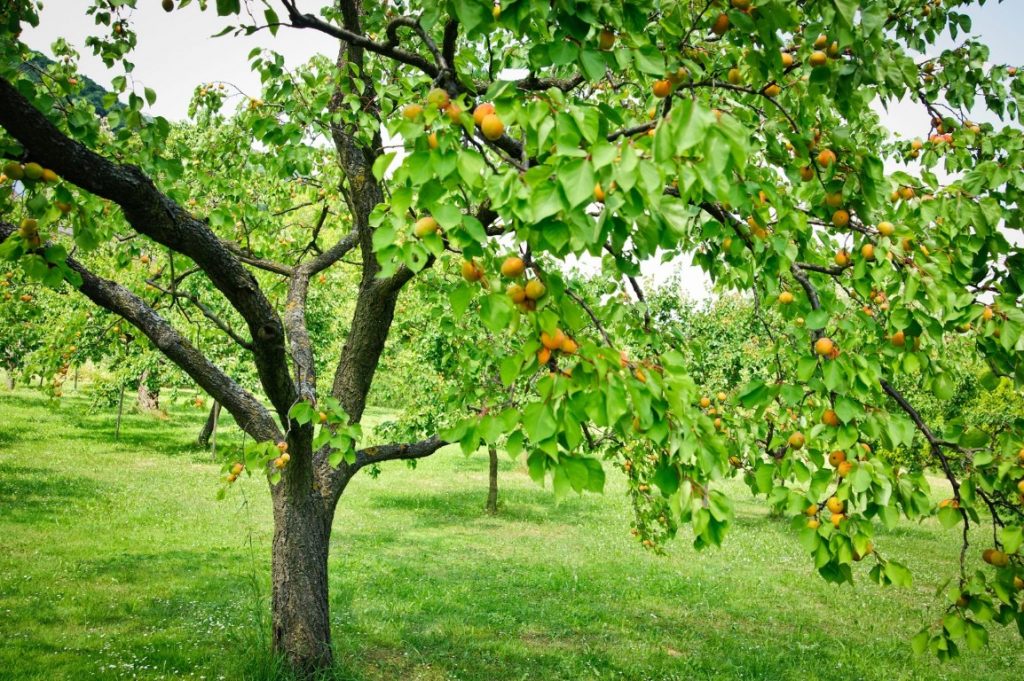
Plant characteristic
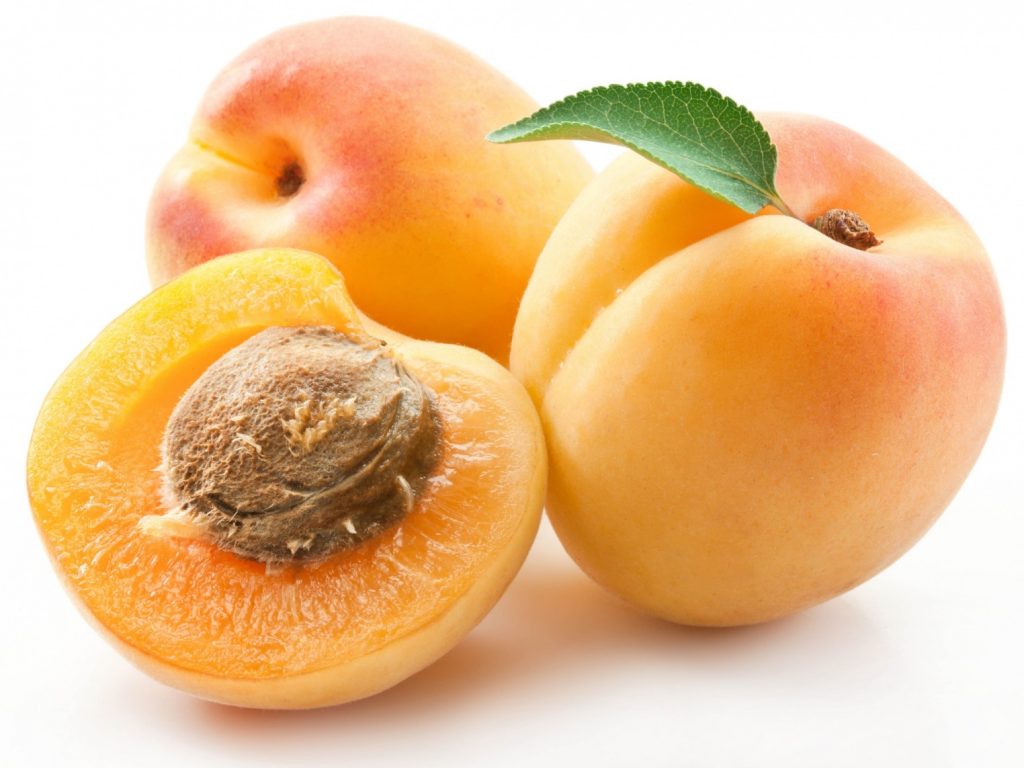
Very often the question arises: is an apricot a fruit or a berry? The unequivocal answer is fruit, because it contains only 1 large stone.
According to the height of the trunk, apricots are of two types:
- dwarf;
- tree-like.
The difference between these two varieties lies in the height of the plant, it varies from 2 to 10 meters. In this case, the root system of the tree goes far into the depths. Depending on the variety, the trunk diameter can reach 60 cm.
The plant is characterized by early fruiting and fast growth. On average, apricot shoots grow by 25-30 cm in 60 days.
Flowering features
The difference with other types of fruit trees lies in the lateral direction of color and fruiting. Blooming usually begins in the lower outer part of the plant. Gradually, the apricot color spreads throughout the tree, then moves to the upper inner part.
The flowers are white or pale pink. The calyx contains 25 stamens and a corolla that includes 5 petals. What does a ripe apricot look like?
Fetus
The fruit receives a bright color due to provitamin A in the composition. The barrel of the berry may be covered in blush.
By size, apricots are divided into 3 groups:
- small-fruited;
- medium-fruited;
- large-fruited.
The fruit has a fleshy sweet pulp. When fully ripe, it separates well from the seed.
Also apricots can be divided according to their shape. The fruits are round, oval and ovoid.
Pollination
Apricot varieties are:
- self-fertile;
- self-infertile;
- partially self-fertile.
Self-pollinating plants give the greatest yield, because they do not depend on the ambient temperature and the presence of bees. In addition, self-fertile apricots do not need a pollinator tree.
Types and varieties of culture
All apricots can be divided into wild and domesticated subspecies. The wild plant can be found in the mountains of Transcaucasia, Central Asia and China. The subspecies is in no way inferior in taste to its domesticated counterparts, which number about 54 varieties.
By origin, the culture can be divided into three types:
- ordinary;
- Manchurian;
- Siberian.
The growing area of the first species stretched from the Tien Shan to Italy. An ordinary tree can reach a height of 12 m. However, it does not tolerate frost well.
The Manchu species, on the other hand, easily tolerates harsh climatic conditions such as drought and frost. The danger for such a tree is a large amount of moisture, which reduces the frost resistance of the plant.
The Siberian species grows in Transbaikalia, China and Mongolia. The dwarf plant grows up to 3m high. The culture adapts well to cold temperatures, it's not for nothing that it is called Siberian.
According to the ripening period, the varieties are divided as follows:
- early maturing;
- mid-season;
- late ripening.
Early maturing culture
The early ripening period provides good adaptation to spring frosts. This is especially important when flowers bloom and fruit set. A special feature of the group is its low height, within 3 meters. Of this species, I would like to note the following varieties:
- Melitopol early. The variety is resistant to diseases and frost. The tree will delight you with large fruits up to 60 g in early July.
- Lel. A low tree 3 m high, begins to bear fruit in the first half of July. The fruit has a bright orange color and weighs up to 30 g.
- Peach. Fruits reach 80 g. It has a consistently high yield. Ripening occurs at the end of July.
Mid-season varieties
They are characterized by high resistance to heat and frost.
- Polesie large-fruited. Partially self-fertile. Fruits in large apricots up to 55 g, not prone to cracking. It tolerates drought and increased rainfall well.
- Pineapple. Fruit of irregular shape, light color with an average fruit weight of 50 g. The variety does not need additional pollinators and is resistant to diseases.
- Triumph. Has a high spreading crown. Ripening begins at the end of July. A self-fertile plant is characterized by rounded fruits weighing up to 60 g.
Late ripening varieties
Late-ripening apricots have dense flesh and are transportable. They can be stored for 1 month. During this time, you can always figure out where to put the juicy and aromatic fruit.
Reproduction of culture
There are several ways to reproduce a tree:
- seed germination;
- graft;
- grafting;
- planting a seedling.
Most trees are cross-pollinated, so it is problematic to determine whether they belong to a particular variety. Using bone propagation, there is no certainty that the exact same plant will grow. To obtain an identical apricot, it is better to use cuttings or grafting. A seedling is the best option if you plan to plant only a single tree in the garden.
How to grow an apricot seedling
Planting a seedling
It is necessary to choose well-lit and warm places protected from the wind. The plant is absolutely undemanding to soil components and nutrients. The main parameter is looseness. Optimal mix:
- sand;
- peat;
- fertile land.
All ingredients in the mixture are taken in equal parts.
Correct bookmark
- A pit is dug with a size of 70 × 70 cm.
- The deepening is covered with prepared soil mixture.
- A seedling is lowered into the hole, deepened, all the roots are straightened. When planting, do not deepen the root collar below surface level.
- The seedling is covered with soil mixture, in the process the tree is shaken to evenly distribute the earth.
- The soil is compacted and a mound is made around the root collar.
- Watering the tree with water around it, without touching the trunk.
- After shrinkage, soil is added and tamped.
How to care for an apricot
Any plant requires complex care, which includes work throughout the season.
Spring works
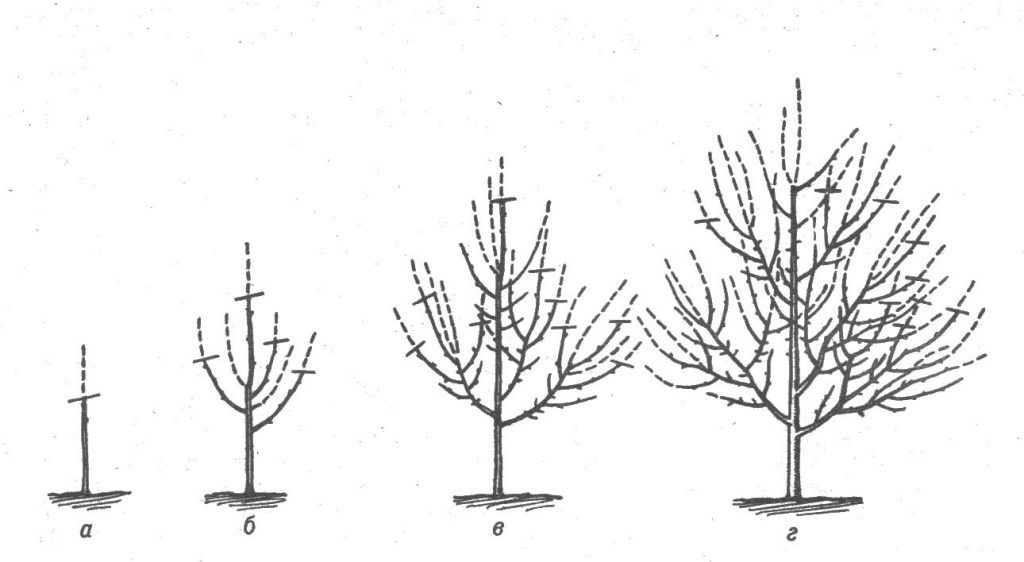
Before the sap flow begins, it is necessary to prune the tree. In the process, dried and frostbitten branches are removed. With the help of pruning, you can form lush crowns and limit crop growth. The tree trunk is whitewashed with lime or covered with special acrylic mixtures.
Spring feeding is done. To do this, you can apply any complex fertilizer under the root. In this case, you can use a nitroammophoska or a mosaic at the rate of 20-40 g for 1 tree, or you can spray with urea on a bare trunk. If the winter was snowless, abundant spring watering of the plant is necessary.
Summer work
During this period, rapid growth occurs. You need to watch how the apricot branches grow. To prevent the crown from thickening, it is necessary to prune. Otherwise, the fruits will not ripen well. You can also do top dressing with ash, it will compensate for the lack of potassium and accelerate ripening. Do not forget about seasonal pest control and mandatory watering during dry summers.
Autumn works
Caring for an apricot in the fall requires the removal of all broken and diseased branches. The soil around the tree is dug up to saturate the roots with air, special autumn fertilizers or superphosphate are applied. These measures allow to successfully endure winter frosts. You also need to carry out preventive work to combat wintering pests.
Diseases and pests
The apricot plant can affect the following diseases:
- monoliotic wilting;
- clasterosporium disease.
The main cause of both diseases is fungus. In the first case, the foliage on the branches begins to dry and mummify. In this case, the fruits are covered with gray rot. The second disease manifests itself on the leaves. First, gray spots are formed, then necrosis. As a result, all apricot leaves are covered with holes.
For prevention and treatment in both cases, you can use Horus 3g per 10 liters or Mobile 4g per 10 liters of water. Processing is carried out on the pink bud and after the fruit set.
The fungus is dangerous because diseases can cause gum flow.The affected areas are cut out, treated with 1% copper sulphate and covered with garden varnish.
Poor apricot harvest can be attributed not only to weather fluctuations or diseases. Irreparable damage to wood can be caused by:
- aphid;
- moth;
- leaf roll.
Aphids are small insects that cover the back of the leaf. They disrupt the photosynthesis of the plant, which leads to a decrease in productivity.
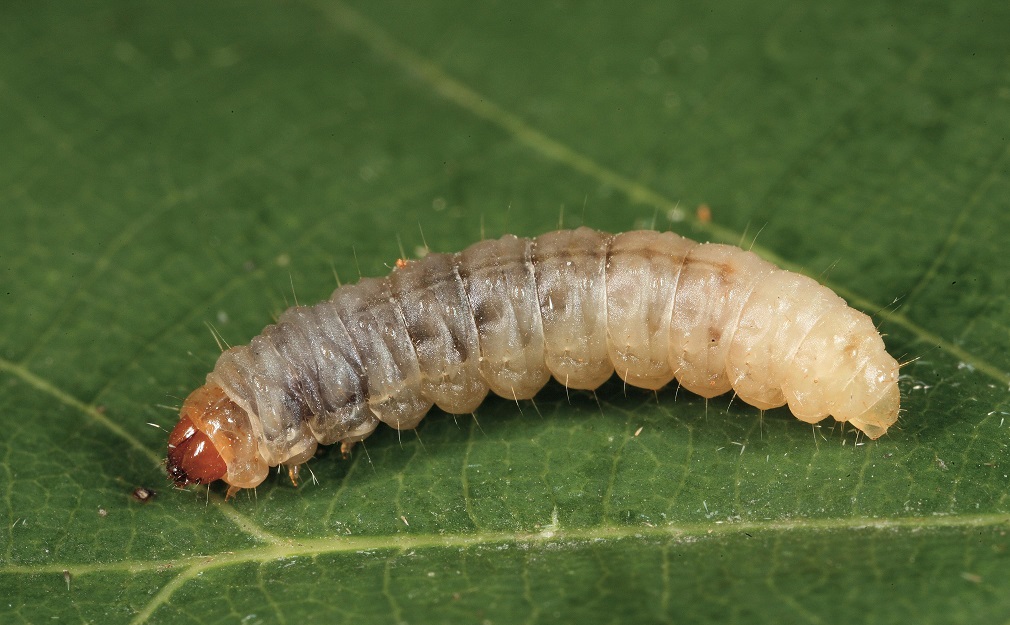
A leafworm is a butterfly that lays its larvae in leaves. Caterpillars devour not only the green mass, but also the buds, disrupting the normal development of the plant.
The moth is a butterfly that lays its eggs in fruits. Caterpillars that developed by the end of summer actively feed on ripening apricots.
Pest control drugs such as enzhio (3.6 ml per 10 l) or presto (3 ml per 5 l of water) help.
Processing is carried out before blooming and on a green leaf. As a preventive measure, it is necessary to carry out a mandatory digging and additional spraying with preparations of the bottom or nitrofen on the bare trunk.
Due to the indices of apricot kbzh and taste, fruit has taken pride of place both in medicine and in cooking. Apricot kernels are also used in recipes.