Content:
A bud mite on currant bushes is considered one of the most dangerous pests for berry crops. The vital activity of the tick on the currant leads to an almost complete loss of yield and the extinction of the bush. The article discusses the kidney mite on currant control measures in spring, a description of the pest, signs of plant disease.
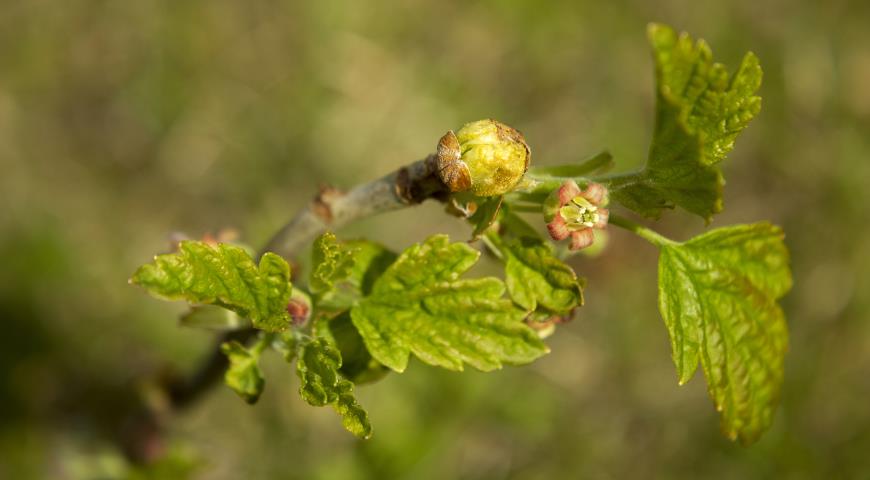
What does a kidney mite look like?
In appearance, the kidney mite resembles a small worm, the size of the body is: 0.2 mm long, 0.04 mm wide. The mite infests the buds of currant bushes. The entire life cycle of the parasite takes place on the plant.
The parasite belongs to the species of four-legged ticks. On the body of the parasite there is a piercing-sucking mouth apparatus, with the help of which the mites feed on the sap of the plant, because of which it dies.
Fertilized female ticks live all winter in currant buds. The "kidney house" protects females from frost and unfavorable weather conditions. In March, when the air temperature warms up to +5 degrees, the female kidney mite begins to lay eggs. They are transparent white in color; as they grow, the color changes to milky white. The shape of the eggs resembles a slightly elongated circle or oval. During the flowering period, mites are selected from the buds.
Having got out, the mites take root on the leaves, bark. Most of the parasites die at this stage. The surviving ticks (approximately 1-2%) move back to the kidneys, where the process of laying eggs resumes. Ticks can exist and develop up to 5 generations while in the bud.
The larva develops inside the egg in 6-12 days. The gluttonous larva gets out through microcracks and settles in healthy buds, begins to suck out the sap of the plant. When attacked by ticks, flower buds receive less nutrition and wither.
During the period of migration, the larvae and females of parasites can be seen when examining the bushes. The kidney mite is transferred to other healthy bushes with the help of wind, rain, human clothing, so it is important to fight the pest in a timely manner.
What harm does it do
The level of harm of the kidney currant mite is the highest among the parasites of horticultural crops. During the spring and summer seasons, the female tick displays up to 40,000 harmful ticks.
The larvae develop in the kidneys, where they are well protected from natural disasters, which complicates the process of destroying pests. If you do not take measures to combat the kidney currant mite, then the bushes of the berry plant can die in one season.
Signs of defeat
Kidney mites reproduce and develop mainly in currant buds. In the fall, the kidneys are deformed, increase in size, in appearance they differ from healthy ones.
Ticks feed on the juice of healthy berry plants.Ticks bring enzymatic substances into the cells of the bushes, provoking a violation of the growth and development of currants.
In the autumn, after the foliage has fallen, the gardener can distinguish between healthy and infected buds:
- Healthy kidneys are round-elongated, develop normally, without signs of damage, outside are covered with dense scales;
- Sick kidneys are deformed, swollen, round in shape, the scales envelop the kidney unevenly. The kidney is swollen due to the large number of parasites that are preparing to winter on the bushes.
Descriptions of affected kidneys that can be seen in spring and summer:
- At the top of young shoots, the shape and color of the leaves change;
- The structure of the leaf blade coarsens, becomes pale green or yellow in color. Leaves are depleted, decrease in volume;
- Bushes with kidney mites are not capable of producing young growth;
- If berries have formed on the currants, then they will be small, sour, the ripening period will be uneven;
- Shoots freeze, stop developing. The plant is affected by diseases of viral origin. Carriers of the virus are kidney ticks. They become the causes of diseases: witch's broom, leaf reversal, double flowers. Parts of plants affected by these diseases must be immediately cut off and burned.
How to deal with a kidney mite on currants
The parasite spends almost all stages of development in the buds of the plant, so it is not easy to destroy the pest. To destroy the bulk of the larvae, it is necessary to treat the bushes with poisonous chemicals during the period of the migration of parasites.
The time of relocation of the larvae coincides with the period of budding and flowering of currants, the use of chemicals at this time is strictly prohibited. Therefore, the processing time of the bushes is transferred until the beginning of flowering or after the complete harvest.
If the bush is severely damaged, the chances that the plant will survive are minimal, and the risk of the parasite spread is high. It is recommended to dig up currant bushes from the root and burn.
Before planting young seedlings, the site is additionally processed. Seedlings should be bought healthy, in proven stores.
Currant mite control methods
There are several ways you can deal with blackcurrant mites:
- Agrotechnical techniques;
- Chemicals;
- Folk remedies;
- Biological method;
- Prevention.
Agrotechnical techniques
With a dense planting of bushes without loosening, watering the soil, the risk of dangerous pests increases. Agrotechnical measures consist of the following tips and recommendations:
- Choose the right site, taking into account the soil requirements for planting young seedlings;
- The crop rotation must be regular;
- The beds must be cleared of weeds, loosened;
- Observe the regime of watering, fertilizing and fertilizing for horticultural crops. These measures improve the resistance of plants to various diseases;
- Purchase quality planting material. Varieties are selected for resistance to diseases and pests;
- It is important that the seedling is not infected even before planting on the site. Treat seedlings before planting. For disinfection, use a solution that you can make yourself. Take 10 liters of water, add 40 g of colloidal sulfur, 10 g of agrovertine, mix the ingredients well. Place the seedling in the solution for a day;
- The larvae do not tolerate high humidity. Therefore, during the period of relocation of larvae, the bushes can be well sprayed with water;
- Visually inspect the bushes for insect pests. When pruning in the spring, check each branch on the bushes. When 2 deformed kidneys are found, they are cut off and burned. If the number of infected buds reaches 6, and they are located in different places, then the branch is cut off completely.If the bush is severely affected by a kidney mite, it must be dug up and burned;
- Every year at the beginning of March, currant bushes can be treated with fire or doused with hot water (+ 70C).
Description of the fire treatment procedure
First, they carry out sanitary pruning of the bush. Using a blowtorch, it is necessary to "burn" the branches of the bush: keeping a distance of 10 cm, quickly move the lamp from top to bottom several times, without holding it in one place. The fire will help to destroy the majority of ticks and aphids, healthy buds and bush will not be affected. This method will not kill 100% of the parasites, but the activity of the ticks will decrease.
How to pour hot water over bushes
You will need a sprinkler with a spray function. Pour boiling water, spray it over the bush at a distance of 20 cm. Hot water will kill fungal pathogens and most of the parasites.
Chemicals
The treatment of bushes at the summer cottage with chemicals must be carried out in accordance with safety precautions, since pesticides are dangerous to humans, animals, birds.
Before starting work, it is imperative to study the effect of the drug, its effectiveness, rules of use, and the frequency of treatments. Failure to follow the instructions for chemicals can harm the plant and others.
Kidney larvae actively develop with the onset of warmth. The higher the temperature, the faster they develop, which means that the processing interval of the bush decreases. For example, at temperatures up to +18 degrees, the development period of the larva is 30 days, the bushes are subject to processing every 12 days. If the air temperature warms up to +30 degrees, then the period of development of the larva passes in 6 days, processing must be carried out every 3 days.
The main three treatments are:
- For the first time, when processing in early spring, bud mites that have wintered on the plant are destroyed;
- The second stage should be carried out at the time of growth and migration of larvae. If you are late with processing, then the larvae develop to an adult, which will again lay eggs for future voracious larvae;
- The third time the procedure is carried out as a safety net. If the females survived, they will cause a new outbreak of currant infection.
Safety measures when working with chemicals:
- Study the instructions for the drug and follow the directions indicated;
- Use rubber gloves, a robe, a hat, a respirator, glasses;
- It is advisable to change the drugs so that there is no addictive effect.
Larvae are most visible and vulnerable during the migration period. At this time, you can use acaricides:
- Contos;
- Vertimek;
- Forbid 4F;
- Endidor;
- Aktelik.
In the fall, when the crop is fully harvested, more aggressive chemicals can be used:
- Nitrofen;
- Phosphamide;
- Rogor-S;
- BI-58.
Folk remedies
Gardeners use folk remedies to save the plant. In early spring, the bushes are treated with decoctions and infusions, which are based on:
- Garlic;
- Onion peel;
- Tobacco;
- Dandelions;
- Mustard;
- Fallen leaves of a walnut.
To make an infusion of dandelion roots and leaves, you need 200 g of roots, 50 g of leaves, 10 liters of water. Peel the roots, chop the leaves and peeled roots, add water, mix, let it brew for 3 hours.
You can make an effective remedy for the parasite from mustard. Take 200 g of mustard powder, pour 10 liters of water. The solution should be infused for 12 hours. Filter the infusion, spray the currant bushes.
To prepare the garlic infusion, you need to take 200 g of garlic cloves, chop (you can use a meat grinder or blender). Pour 10 liters of water over the gruel, let it brew for several hours. Filter the infusion through cheesecloth, spray the currants with the solution.
Ticks do not tolerate the smell of garlic and onions, so these plants can be planted in an area with currant bushes. Mites will not multiply in the vicinity of garlic and onions.If chemical preparations were used to control ticks, then garlic and onions are not recommended for food.
The use of biological products
The use of biological preparations, which are based on positive strains of bacteria and fungi, is not dangerous for humans.
To combat ticks, use:
- Bioacaricides;
- Bioinsectoacaricides.
Biologics are effective in warm, windless weather. In early warm spring, the effect of the drug is most noticeable.
Popular bioacaricides:
- Akarin;
- Fitoferm;
- Boverin;
- Bicol.
Prevention
A bud mite is difficult to remove if it has settled on a bush, it is easier to prevent the appearance of a pest. To do this, the gardener needs:
- Choose varieties of currants that are resistant to diseases;
- Buy young seedlings only in special nurseries;
- Disinfect the planting material before landing on the site;
- Conduct a thorough inspection of the bush, if pests are found, destroy them;
- Uproot and burn infected bushes;
- Treat bushes with biological and chemical agents.
Resistant blackcurrant varieties:
- Minx;
- Riddle;
- Memory of Michurin;
- Nightingale night;
- Sevchanka.
Methods for controlling kidney mites differ in effectiveness and harm to the environment. Based on the stage of damage to the bush, it is important to choose the best method to destroy the insect. You should not immediately resort to the help of harsh chemicals, as they will destroy along with pests and beneficial insects. Knowing the ways of prevention, you can avoid problems with parasites in the future. Have a good harvest!